This challenging question on normal distribution was posted in Edusnap by a student.
There were two mistakes made:
1) Interpreting the distribution of 2 large hampers and n small hampers as 2L + nS.
2) Calculation of variance
Here is the correct solution:
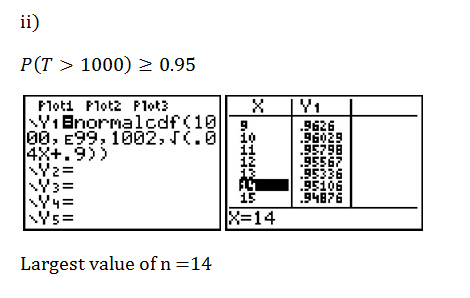
Smallest possible value of n = 9
————————-
When the question mentions n items, the distribution is X1+X2+…Xn. When the question asks for “n times of a randomly chosen..”, then the distribution is nX.
Students also need to be familiar with calculating the expectation and variance of the sum or difference of normal distribution using the formula:




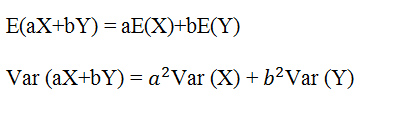


















You must be logged in to post a comment.