The answer is no. Correct answer is 
See the following example how this concept is applied in H2 math
Example 1
Differentiate 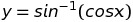 with respect to x
with respect to x
Therefore
Ans: -1 if sin x > 0, 1 if sin x < 0
Example 2
In how many ways can 9 balls of which 4 are red, 4 are white and 1 black be arranged in a line so that no red ball is next to the black?
Answer: 175
Solution
Case 1: 1st ball is black in the whole row of 9 balls
Then the 2nd ball must be white. The rest of the 4 red and 3 white balls can be arranged in  = 35 ways
= 35 ways
Case 2: last ball is black
Then the 2nd last ball must be white. The rest of the 4 red and 3 white balls can be arranged in  = 35 ways
= 35 ways
Case 3: Black ball is not the 1st or last ball
Then the black ball must be between 2 white balls. Consider WBW as one unit. Together with 4 red balls and 2 white balls, these can arranged in  = 105 ways
= 105 ways
Using the addition principle, total number of ways = 35+35+105= 175
GC can be very helpful in solving certain problems in Complex Numbers.
Example 1
Use the GC to find the real value of k such that 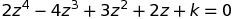 has a complex root 1-i.
has a complex root 1-i.
Solution
Since 1-i is a root,
Using TI 84 Plus (OS 2.55) to evaluate the complex numbers, we have
2+k = 0
k=-2
Example 2
Solution
Since the equation is quadratic, we can use the quadratic formula.
Using the GC to evaulate the above,
z = 1+2i or -7i
At Nuts supermarket, a discount is offered on Almonds, Cashew and Walnuts if more than a certain weight of it is bought. On a particular grocery shopping trip, King Kong bought a total of 12 kg of nuts as follows:
| Types of Nut | Price per kg ($) | Discount offered |
| Almond | 14 | 20% for more than 6 kg bought |
| Cashew | 9 | 15% for more than 3 kg bought |
| Walnuts | 11 | 10% for more than 2 kg bought |
King Kong bought at least 3.5 kg of each type of nut and spent $124.03 after an overall discount of $10.17. Find the weight of each type of nut King Kong bought from the supermarket.
Solution
We know that discount is obtained from the purchase of cashew and walnuts, since the amount bought is at least 3.5 kg of each type. However, we do not know whether any discount is obtained for the purchase of almonds.
Therefore, we make the assumption that the amount of almonds bought is less than or equal to 6kg, and hence no discount. If the solution turns out to be between 3.5 to 6kg inclusive, we accept the solution. Else we reject and change the assumption to almonds bought is greater than 6kg, reformulate and solve the equations again.
Let a, b and c be the number of kg of almonds, cashew and walnuts bought respectively.
Therefore a+b+c= 12 (Eqn 1)
14a+b(0.85×9)+c(0.9×11)=124.03
14a+7.65b+9.9c=124.03 (Eqn 2)
0.15x9b+0.1x11c=10.17
1.35b+1.1c= 10.17 (Eqn 3)
Solving the 3 equations with GC,
a= 3.8 , b=4.6, c=3.6
Since a is between 3.5 to 6, our assumption and hence solution is valid.
King Kong bought 3.8 kg of almonds, 4.6 kg of cashew and 3.6 kg of walnuts.
There are a total of 20 amusement rides in a theme park. A child insists on trying at least 5 of the amusement rides. Calculate the number of ways in which this can be done.
Answer: 1042380
Solution
Method 1
20 choose 5 + 20 choose 6 +… 20 choose 20
Using TI 84 OS (2.55)
sum (seq(20 nCr X, X, 5, 20, 1)
= 1042380
Method 2
2^20- (20 choose 0+ 20 choose 1+20 choose 2+20 choose 3+ 20 choose 4)
=1042380
(i) find the Maclaurin’s series of f(x) up to and including the term in 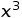 .
.
(ii) Hence deduce the series expansion of the function 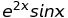 up to and including the term in
up to and including the term in 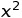
Solution
(i) is routine, can easily work out to be
(ii) requires Higher Order Thinking (HOT)
We differentiate the series obtained in (i) to get 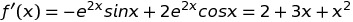
Principle used: Differentiate one series expansion to get the series expansion for another series.
You must be logged in to post a comment.