Category: 1. H2 maths tips (9758)
Challenging Normal Distribution problem 2
Juggling: shortcut to long division
Triangular permutations
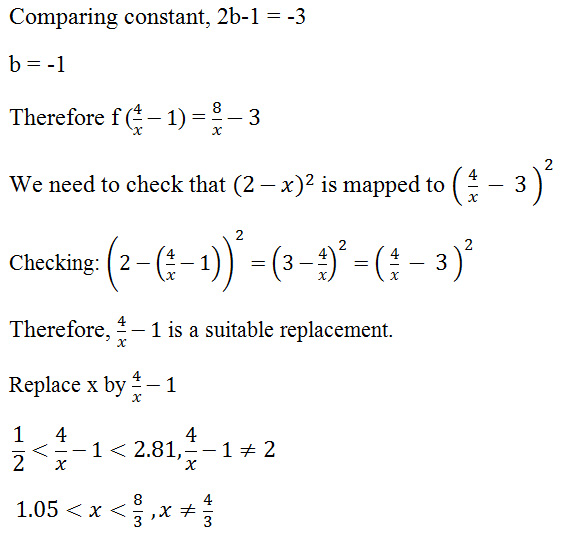
Finding suitable replacement to solve new inequalities
Graph transformation of oblique asymptote
Many students have difficulty with the graph transformation of oblique asymptote. Consider the oblique asymptote y = x-1 (red line)
i) y= 1/ f(x)
f(x) approaches infinity as x approaches infinity. 1 divided by infinity is 0.
Hence oblique asymptote y=x-1 becomes horizontal asymptote y= 0
For y= 1/ f(x), any oblique asymptote y=ax+b in f(x) will become horizontal asymptote y= 0
ii) y= f ‘ (x)
The gradient of y= x-1 is 1. Hence oblique asymptote y=x-1 becomes horizontal asymptote y= 1
For y= f ‘ (x), any oblique asymptote y=ax+b in f(x) will become horizontal asymptote y= a
iii) y= f(2x+1)
Let original asymptote be f(x) = x-1
Therefore, f(2x+1) = (2x+1)-1 = 2x
Hence oblique asymptote y = x-1 is transformed to y=2x.
This method can be applied to any oblique asymptote.
Circular Permutations
Circular permutations often pose some difficulty to students. Let’s consider the following scenarios:
Scenario A: 10 people to be seated at a round table with 10 identical seats
Number of ways = (10-1)! = 9! = 362880
Scenario B: 5 people to be seated at a round table with 10 numbered seats
Number of ways = 10 P 5 = 30240
Scenario C: 6 people to be seated at a round table with 10 identical seats
There will be 4 identical empty seats. Consider fixing 1 occupied seat, and permutate the other 9 seats around it. There are 4 identical seats among the 9 seats. So number of ways = 9!/4! = 15120
Challenging Permutation question 5
A tennis club has n male players and n female players. For a tournament the players are to be arranged in n pairs, with each pair consisting of one male and one female. Find the number of possible pairings.
Answer: n!
Solution
Suppose the male got to choose his partner. The first male can choose from n females. After he has chosen, the next male can choose from (n-1) females. So the number of possible pairings is n.(n-1).(n-2)…1 = n!
For instance there are 2 male players (M1, M2) and 2 female (F1, F2) players.
One way to arrange 2 pairs of players: M1 F1 and M2 F2
Second way to arrange 2 pairs of players: M1 F2 and M2 F1
Number of ways to arrange 2 pairs of players is 2!
Comments
Some students will give the wrong answer n x n, which is the number of ways to choose a pair.
How to revise during the school holidays?
Go through the exam paper and prioritise the topics according to the number of marks lost. Start by revising the topic with the most number of marks lost. Do correction without copying solution and do 1 or 2 more similar questions until can do correctly within time limit of 1.5 min/mark. If score 0 in that topic, practice 10 questions in that topic. After topical revision, do a practice paper under exam condition. Repeat the cycle of paper topical until can achieve your desired grade.
Focus on brushing up Calculus, Sequence and Series, Vectors and Complex Numbers. These four major modules account for more than 60% of marks in A level.
Can engage a good tutor to shorten the learning cycle.
Doing tutorials is not enough!
For the average JC H2 maths student, doing tutorials alone is not enough to pass mid year or promo exams. This is because many JCs set the exams at a much higher standard than tutorials. In some JCs, about half of the cohort can fail JC 1 promo.
To do well, other than doing tutorials, students need to practise intermediate or advanced questions. If they are unable to do intermediate questions, they should seek help early from a good tutor.
If students fail or barely pass their mid year or promo, don’t wait until JC 2 to brush up. Otherwise, they have to struggle to catch up and learn new challenging topics in year 2.



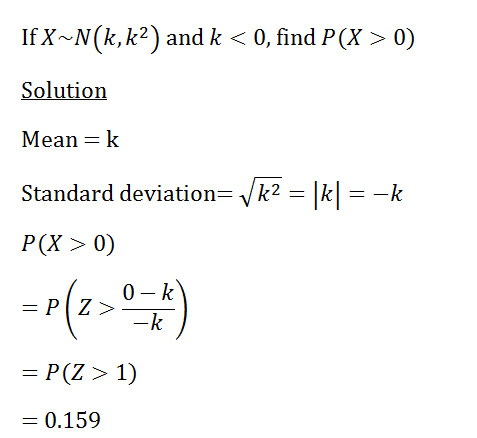






You must be logged in to post a comment.